A "combinatorial dimension" geometry. More...
#include <egs_cd_geometry.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| EGS_CDGeometry (EGS_BaseGeometry *G1, EGS_BaseGeometry **G, const string &Name="", int indexing=0) | |
| EGS_CDGeometry (EGS_BaseGeometry *G1, const vector< EGS_BaseGeometry * > &G, const string &Name="", int indexing=0) | |
| int | medium (int ireg) const |
| bool | isRealRegion (int ireg) const |
| bool | isInside (const EGS_Vector &x) |
| int | isWhere (const EGS_Vector &x) |
| int | inside (const EGS_Vector &x) |
| int | howfar (int ireg, const EGS_Vector &x, const EGS_Vector &u, EGS_Float &t, int *newmed=0, EGS_Vector *normal=0) |
| EGS_Float | hownear (int ireg, const EGS_Vector &x) |
| int | getMaxStep () const |
| void | getNextGeom (EGS_RandomGenerator *rndm) |
| void | updatePosition (EGS_Float time) |
| void | containsDynamic (bool &hasdynamic) |
| bool | hasBooleanProperty (int ireg, EGS_BPType prop) const |
| void | setBooleanProperty (EGS_BPType) |
| void | addBooleanProperty (int) |
| void | setBooleanProperty (EGS_BPType, int, int, int step=1) |
| void | addBooleanProperty (int, int, int, int step=1) |
| const string & | getType () const |
| void | setRelativeRho (int start, int end, EGS_Float rho) |
| void | setRelativeRho (EGS_Input *) |
| EGS_Float | getRelativeRho (int ireg) const |
| void | setBScaling (int start, int end, EGS_Float bf) |
| void | setBScaling (EGS_Input *) |
| EGS_Float | getBScaling (int ireg) const |
| virtual void | getLabelRegions (const string &str, vector< int > ®s) |
 Public Member Functions inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry Public Member Functions inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry | |
| EGS_BaseGeometry (const string &Name) | |
| Construct a geometry named Name. More... | |
| virtual | ~EGS_BaseGeometry () |
| Destructor. More... | |
| bool | isConvex () const |
| Is the geometry convex? More... | |
| virtual EGS_Float | howfarToOutside (int ireg, const EGS_Vector &x, const EGS_Vector &u) |
| virtual EGS_Float | getVolume (int ireg) |
| Calculates the volume of region ireg. More... | |
| virtual EGS_Float | getBound (int idir, int ind) |
| Returns region boundaries in direction determined by idir. More... | |
| virtual int | getNRegDir (int idir) |
| int | regions () const |
| Returns the number of local regions in this geometry. More... | |
| virtual int | computeIntersections (int ireg, int n, const EGS_Vector &x, const EGS_Vector &u, EGS_GeometryIntersections *isections) |
| Calculates intersection distances to region boundaries. More... | |
| void | setMedium (const string &Name) |
| Set all regions to a medium with name Name. More... | |
| void | setMedium (int start, int end, const string &Name, int delta=1) |
| Set every delta'th region between start and end to the medium named Name. More... | |
| void | setMedium (int imed) |
| Set all regions to a medium with index imed. More... | |
| void | setMedium (int istart, int iend, int imed, int delta=1) |
| Set every delta'th region between start and end (inclusive) to imed. More... | |
| void | setMedia (EGS_Input *inp) |
| Set the media in the geometry from the input pointed to by inp. More... | |
| bool | hasRhoScaling () const |
| Does this geometry object have a mass density scaling feature? | |
| EGS_Float | getMediumRho (int ind) const |
| virtual void | setApplication (EGS_Application *app) |
| bool | hasBScaling () const |
| Does this geometry object have a B field scaling feature? | |
| const string & | getName () const |
| Get the name of this geometry. More... | |
| void | setDebug (bool deb) |
| Turn debugging on. More... | |
| void | setName (EGS_Input *inp) |
| Set the name of the geometry from the input inp. More... | |
| void | setBoundaryTolerance (EGS_Input *inp) |
| Set the value of the boundary tolerance from the input inp. More... | |
| void | setBoundaryTolerance (EGS_Float tol) |
| Set the value of the boundary tolerance from argument. | |
| virtual void | printInfo () const |
| Print information about this geometry. More... | |
| int | ref () |
| Increase the reference count to this geometry. More... | |
| int | deref () |
| Decrease the reference count to this geometry. More... | |
| EGS_Float | getBoundaryTolerance () |
| Get the value of the boundary tolerance. | |
| virtual void | getNumberRegions (const string &str, vector< int > ®s) |
| Get a list of all the regions labeled with a number. | |
| virtual const string & | getLabelName (const int i) |
| Get the name of the i-th explicit label in the geometry. | |
| virtual int | getLabelCount () |
| Get the number of explicit labels in the geometry. | |
| int | setLabels (EGS_Input *input) |
| Set the labels from an input block. | |
| int | setLabels (const string &inp) |
| Set the labels from an input string. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | setMedia (EGS_Input *inp, int, const int *) |
Protected Attributes | |
| EGS_BaseGeometry * | bg |
| EGS_BaseGeometry ** | g |
| int | nbase |
| int | nmax |
| bool | new_indexing |
| int * | reg_to_base |
| int * | local_start |
 Protected Attributes inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry Protected Attributes inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry | |
| int | nreg |
| Number of local regions in this geometry. More... | |
| string | name |
| Name of this geometry. More... | |
| short * | region_media |
| Array of media indeces. More... | |
| int | med |
| Medium index. More... | |
| bool | has_rho_scaling |
| Does this geometry have relative mass density scvaling? | |
| EGS_Float * | rhor |
| Array with relative mass densities. | |
| bool | has_B_scaling |
| Does this geometry has B field scaling factor? | |
| bool | has_Ref_rho |
| EGS_Float * | bfactor |
| Array with B field scaling factors. | |
| EGS_Float | rhoRef |
| Reference density for B field scaling. | |
| int | nref |
| Number of references to this geometry. More... | |
| bool | debug |
| Debugging flag. More... | |
| bool | is_convex |
| Is this geometry convex? More... | |
| EGS_BPType | bproperty |
| A bit mask of boolean properties for the entire geometry. More... | |
| EGS_BPType * | bp_array |
| An array of boolean properties on a region by region basis. More... | |
| EGS_Float | boundaryTolerance |
| Boundary tolerance for geometries that need it. | |
| EGS_Float | halfBoundaryTolerance |
| vector< label > | labels |
| Labels. More... | |
| EGS_Application * | app |
| The application this object belongs to. | |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static string | type = "EGS_CDGeometry" |
 Static Protected Attributes inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry Static Protected Attributes inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry | |
| static int | error_flag = 0 |
| Set to non-zero status if a geometry problem is encountered. | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry Static Public Member Functions inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry | |
| static int | findRegion (EGS_Float xp, int np, const EGS_Float *p) |
| Find the bin to which xp belongs, given np bin edges p. More... | |
| static int | nMedia () |
| Get the number of media registered so far by all geometries. More... | |
| static const char * | getMediumName (int ind) |
| Get the name of medium with index ind. More... | |
| static int | addMedium (const string &medname) |
| Add a medium or get the index of an existing medium. More... | |
| static int | getMediumIndex (const string &medname) |
| Get the index of a medium named medname. More... | |
| static EGS_BaseGeometry * | createGeometry (EGS_Input *) |
| Create a geometry (or geometries) from a given input. More... | |
| static EGS_BaseGeometry * | createSingleGeometry (EGS_Input *inp) |
| Create a single geometry from the input inp. More... | |
| static void | clearGeometries () |
| Clears (deletes) all geometries in the currently active geometry list. More... | |
| static EGS_BaseGeometry * | getGeometry (const string &Name) |
| Get a pointer to the geometry named Name. More... | |
| static EGS_BaseGeometry ** | getGeometries () |
| static int | getNGeometries () |
| static string | getUniqueName () |
| Get a unique geometry name. More... | |
| static void | describeGeometries () |
| Describes all existing geometries. More... | |
| static void | setActiveGeometryList (int list) |
| Set the currently active geometry list. | |
| static int | getLastError () |
| static void | resetErrorFlag () |
Detailed Description
A "combinatorial dimension" geometry.
The name of this geometry type is not very intuitive but resulted from an early, much less general implementation, which was called a "combinatorial dimension" (CD) geometry. For a lack of a better name, the CD notation was kept. A CD geometry consists of a base geometry ![]() , which defines
, which defines ![]() regions. For each of the
regions. For each of the ![]() regions there are geometries
regions there are geometries ![]() , which divide the
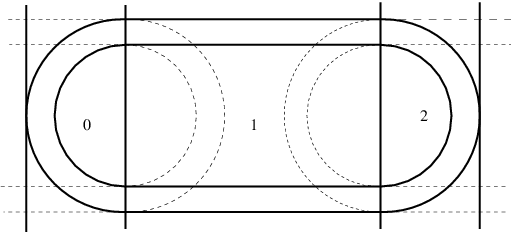
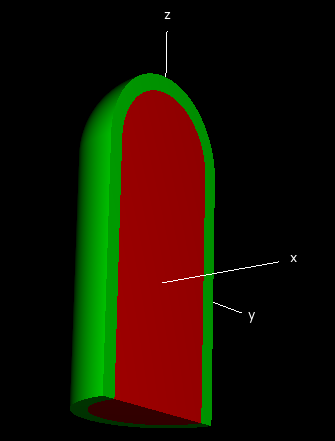
, which divide the ![]() regions into additional regions. As an example, consider a set of 4 parallel planes that defines 3 regions. In region 0 there is a set of 2 spheres, in region 1 a set of 2 cylinders and in region 2 another set of 2 spheres to define a cylindrical structure with rounded ends as shown in
the following figure
regions into additional regions. As an example, consider a set of 4 parallel planes that defines 3 regions. In region 0 there is a set of 2 spheres, in region 1 a set of 2 cylinders and in region 2 another set of 2 spheres to define a cylindrical structure with rounded ends as shown in
the following figure
As another example consider a set of 2 cylinders defining 2 regions. In region 0 (within the inner cylinder) there is a set of ![]() parallel planes that define
parallel planes that define ![]() regions and in region 1 of the base cylinder there is a set of just 2 planes that defines a single region, as shown in
the following figure
regions and in region 1 of the base cylinder there is a set of just 2 planes that defines a single region, as shown in
the following figure
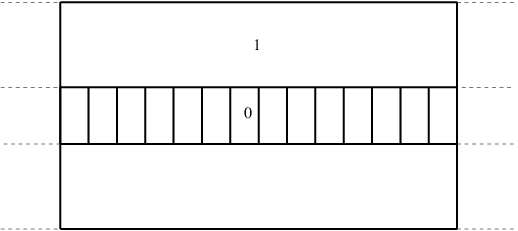
One could use the second geometry to calculate the depth dose curve of a beam incident from the top, for instance. The CD geometry type is very versatile and can be used to model a wide range of geometrical structures. It is therefore important to understand the logic behind the various geometry methods, which is as follows:
- A point is inside a CD geometry if it is inside
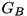 and in addition it is inside the geometry for the region of
and in addition it is inside the geometry for the region of 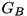 in which the point is, if there is such a geometry defined (note: it is possible that a region of the CD geometry does not have an additional geometry defined).
in which the point is, if there is such a geometry defined (note: it is possible that a region of the CD geometry does not have an additional geometry defined). - If a point is in region
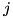 of
of 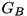 and in region
and in region 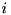 of
of 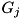 (the geometry belonging to region
(the geometry belonging to region 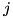 of
of 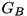 ), the region index in the CD geometry is
), the region index in the CD geometry is 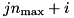 , where
, where 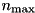 is the maximum number of regions for each of the
is the maximum number of regions for each of the 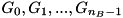 .
. - If the particle is inside a CD geometry in
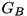 region
region 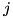 , then the distance to a boundary is the minimum of the distances to a boundary in
, then the distance to a boundary is the minimum of the distances to a boundary in 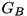 and
and 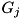 . If the particle first crosses a boundary in
. If the particle first crosses a boundary in 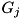 , the new region on the other side of the boundary is either
, the new region on the other side of the boundary is either 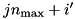 , if the new region
, if the new region 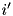 is still inside of
is still inside of 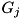 , or -1 if the particle exits
, or -1 if the particle exits 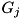 . If the particle first crosses a boundary in
. If the particle first crosses a boundary in 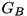 into a region
into a region 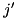 , then the new region is either
, then the new region is either 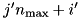 , if the new position is in region
, if the new position is in region 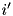 inside of
inside of 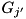 , or -1, if the new position is outside of
, or -1, if the new position is outside of 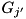
- If a particle is outside of a CD geometry, then the distance to a boundary is calculated by following the trajectory until it either enters a region
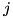 of
of 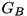 that is already inside of
that is already inside of 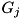 or enters a geometry in one of the regions of
or enters a geometry in one of the regions of 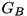 .
. - When a particle is inside of a CD geometry in
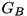 region
region 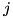 , then
, then 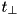 is given by the minimum of
is given by the minimum of 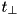 from
from 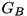 and from
and from 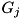
- When a particle is outside of a CD geometry, then
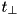 is given by the
is given by the 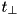 of
of 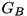 , if the position is outside of
, if the position is outside of 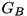 , or by the minimum of the perpendicular distances to
, or by the minimum of the perpendicular distances to 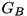 and
and 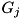 , if the particle is inside of region
, if the particle is inside of region 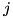 in
in 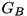 (but is obviously outside of
(but is obviously outside of 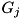 ).
).
Note that in many cases geometry objects that can be modeled as CD geometries could also be modeled as unions with appropriately assigned priorities (see EGS_UnionGeometry). However, due to the fact that in the CD geometries only checks against a single geometry in addition to ![]() are required, it is likely that a CD model will be much more efficient than a union model. For instance, the geometry shown in
the first figure
can be modeled as the union of two sets of spheres and an N-dimensional geometry made from a set of two cylinders and a set of two planes for the middle portion by giving the N-dimensional geometry a higher priority than the sets of spheres.
are required, it is likely that a CD model will be much more efficient than a union model. For instance, the geometry shown in
the first figure
can be modeled as the union of two sets of spheres and an N-dimensional geometry made from a set of two cylinders and a set of two planes for the middle portion by giving the N-dimensional geometry a higher priority than the sets of spheres.
A CD geometry is defined in the input file using the following key-pair values
library = egs_cdgeometry base geometry = name of a previously defined geometry set geometry = region1, name of a previously defined geometry set geometry = region2, name of a previously defined geometry ...
If the same geometry divides several consecutive regions, one can use
set geometry = start region, stop region, name of a previously defined geometry
There can be an arbitrary number of set geometry keys.
As concluding remark for the CD geometry type, it is worth noting that the treatment head of a medical linear accelerator can be efficiently modeled with the help of a CD geometry. This can be seen in the photon_linac.geom example geometry file. Many of the other examples also employ a CD-geometry.
A simple example:
:start geometry definition:
# The base geometry, this will be the Chopping Device (CD)
# The base geometry can be any geometry, even a composite one
:start geometry:
name = my_cd_planes
library = egs_planes
type = EGS_Zplanes
positions = -3 3 5
# No media required
:stop geometry:
:start geometry:
name = my_cd_cylinder
library = egs_cylinders
type = EGS_ZCylinders
radii = 1.6 2
:start media input:
media = air water
set medium = 1 1
:stop media input:
:stop geometry:
:start geometry:
name = my_cd_sphere
library = egs_spheres
midpoint = 0 0 3
radii = 1.6 2
:start media input:
media = air water
set medium = 1 1
:stop media input:
:stop geometry:
# The composite geometry
:start geometry:
name = my_cd
library = egs_cdgeometry
base geometry = my_cd_planes
# set geometry = 1 geom means:
# "in region 1 of the basegeometry, use geometry "geom"
set geometry = 0 my_cd_cylinder
set geometry = 1 my_cd_sphere
# The final region numbers are attributed by the cd geometry object;
# Use the viewer to determine region numbers
:stop geometry:
simulation geometry = my_cd
:stop geometry definition:
Definition at line 265 of file egs_cd_geometry.h.
Member Data Documentation
◆ new_indexing
|
protected |
If true, use new indexing style
Definition at line 920 of file egs_cd_geometry.h.
◆ reg_to_base
|
protected |
If new indexing style is used, converts global region to base region
Definition at line 923 of file egs_cd_geometry.h.
◆ local_start
|
protected |
If new indexing style is used, local_start[ibase] is the first region in base region ibase
Definition at line 926 of file egs_cd_geometry.h.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- /home/rwtownson/EGSnrc/HEN_HOUSE/egs++/geometry/egs_cd_geometry/egs_cd_geometry.h
- /home/rwtownson/EGSnrc/HEN_HOUSE/egs++/geometry/egs_cd_geometry/egs_cd_geometry.cpp
 1.9.1
1.9.1