A class modeling a N-dimensional geometry. More...
#include <egs_nd_geometry.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| EGS_NDGeometry (int ng, EGS_BaseGeometry **G, const string &Name="", bool O=true) | |
| EGS_NDGeometry (vector< EGS_BaseGeometry * > &G, const string &Name="", bool O=true) | |
| bool | isInside (const EGS_Vector &x) |
| int | isWhere (const EGS_Vector &x) |
| int | inside (const EGS_Vector &x) |
| EGS_Float | howfarToOutside (int ireg, const EGS_Vector &x, const EGS_Vector &u) |
| int | howfar (int ireg, const EGS_Vector &x, const EGS_Vector &u, EGS_Float &t, int *newmed=0, EGS_Vector *normal=0) |
| EGS_Float | hownear (int ireg, const EGS_Vector &x) |
| int | getMaxStep () const |
| void | getNextGeom (EGS_RandomGenerator *rndm) |
| void | updatePosition (EGS_Float time) |
| void | containsDynamic (bool &hasdynamic) |
| const string & | getType () const |
| void | printInfo () const |
| virtual void | getLabelRegions (const string &str, vector< int > ®s) |
| void | ndRegions (int r, int dim, int dimk, int k, vector< int > ®s) |
 Public Member Functions inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry Public Member Functions inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry | |
| EGS_BaseGeometry (const string &Name) | |
| Construct a geometry named Name. More... | |
| virtual | ~EGS_BaseGeometry () |
| Destructor. More... | |
| bool | isConvex () const |
| Is the geometry convex? More... | |
| virtual EGS_Float | getVolume (int ireg) |
| Calculates the volume of region ireg. More... | |
| virtual EGS_Float | getBound (int idir, int ind) |
| Returns region boundaries in direction determined by idir. More... | |
| virtual int | getNRegDir (int idir) |
| int | regions () const |
| Returns the number of local regions in this geometry. More... | |
| virtual bool | isRealRegion (int ireg) const |
| Returnes true if ireg is a real region, false otherwise. More... | |
| virtual int | medium (int ireg) const |
| Returns the medium index in region ireg. More... | |
| virtual int | computeIntersections (int ireg, int n, const EGS_Vector &x, const EGS_Vector &u, EGS_GeometryIntersections *isections) |
| Calculates intersection distances to region boundaries. More... | |
| void | setMedium (const string &Name) |
| Set all regions to a medium with name Name. More... | |
| void | setMedium (int start, int end, const string &Name, int delta=1) |
| Set every delta'th region between start and end to the medium named Name. More... | |
| void | setMedium (int imed) |
| Set all regions to a medium with index imed. More... | |
| void | setMedium (int istart, int iend, int imed, int delta=1) |
| Set every delta'th region between start and end (inclusive) to imed. More... | |
| void | setMedia (EGS_Input *inp) |
| Set the media in the geometry from the input pointed to by inp. More... | |
| bool | hasRhoScaling () const |
| Does this geometry object have a mass density scaling feature? | |
| virtual EGS_Float | getRelativeRho (int ireg) const |
| Get the relative mass density in region ireg. | |
| virtual void | setRelativeRho (int start, int end, EGS_Float rho) |
| Set the relative mass density in regions. More... | |
| virtual void | setRelativeRho (EGS_Input *) |
| Set the relative mass density from an user input. More... | |
| EGS_Float | getMediumRho (int ind) const |
| virtual void | setApplication (EGS_Application *app) |
| bool | hasBScaling () const |
| Does this geometry object have a B field scaling feature? | |
| virtual EGS_Float | getBScaling (int ireg) const |
| Get the B field scaling factor in region ireg. | |
| virtual void | setBScaling (int start, int end, EGS_Float bf) |
| Set the B field scaling factor in regions. More... | |
| virtual void | setBScaling (EGS_Input *) |
| Set the B field scaling factor from an user input. More... | |
| const string & | getName () const |
| Get the name of this geometry. More... | |
| void | setDebug (bool deb) |
| Turn debugging on. More... | |
| void | setName (EGS_Input *inp) |
| Set the name of the geometry from the input inp. More... | |
| void | setBoundaryTolerance (EGS_Input *inp) |
| Set the value of the boundary tolerance from the input inp. More... | |
| void | setBoundaryTolerance (EGS_Float tol) |
| Set the value of the boundary tolerance from argument. | |
| virtual bool | hasBooleanProperty (int ireg, EGS_BPType prop) const |
| Is the boolean property prop set for region ireg ? | |
| virtual void | setBooleanProperty (EGS_BPType prop) |
| Set the boolean properties of the entire geometry to prop. More... | |
| virtual void | addBooleanProperty (int bit) |
| Add a boolean property for the entire geometry by setting the bit'th bit. More... | |
| virtual void | setBooleanProperty (EGS_BPType prop, int start, int end, int step=1) |
| Set the boolean properties of every step'th region between start and end (inclusive) to prop. More... | |
| virtual void | addBooleanProperty (int bit, int start, int end, int step=1) |
| Add a boolean property to every step'th region between start and end (inclusive) by setting the bit'th bit. More... | |
| int | ref () |
| Increase the reference count to this geometry. More... | |
| int | deref () |
| Decrease the reference count to this geometry. More... | |
| EGS_Float | getBoundaryTolerance () |
| Get the value of the boundary tolerance. | |
| virtual void | getNumberRegions (const string &str, vector< int > ®s) |
| Get a list of all the regions labeled with a number. | |
| virtual const string & | getLabelName (const int i) |
| Get the name of the i-th explicit label in the geometry. | |
| virtual int | getLabelCount () |
| Get the number of explicit labels in the geometry. | |
| int | setLabels (EGS_Input *input) |
| Set the labels from an input block. | |
| int | setLabels (const string &inp) |
| Set the labels from an input string. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | setup () |
| void | setMedia (EGS_Input *inp, int nmed, const int *med_ind) |
| Define media. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| int | N |
| Number of dimensions. | |
| EGS_BaseGeometry ** | g |
| The dimensions. | |
| int * | n |
| Used for calculating region indeces. | |
| bool | ortho |
| Is the geometry orthogonal ? | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry Protected Attributes inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry | |
| int | nreg |
| Number of local regions in this geometry. More... | |
| string | name |
| Name of this geometry. More... | |
| short * | region_media |
| Array of media indeces. More... | |
| int | med |
| Medium index. More... | |
| bool | has_rho_scaling |
| Does this geometry have relative mass density scvaling? | |
| EGS_Float * | rhor |
| Array with relative mass densities. | |
| bool | has_B_scaling |
| Does this geometry has B field scaling factor? | |
| bool | has_Ref_rho |
| EGS_Float * | bfactor |
| Array with B field scaling factors. | |
| EGS_Float | rhoRef |
| Reference density for B field scaling. | |
| int | nref |
| Number of references to this geometry. More... | |
| bool | debug |
| Debugging flag. More... | |
| bool | is_convex |
| Is this geometry convex? More... | |
| EGS_BPType | bproperty |
| A bit mask of boolean properties for the entire geometry. More... | |
| EGS_BPType * | bp_array |
| An array of boolean properties on a region by region basis. More... | |
| EGS_Float | boundaryTolerance |
| Boundary tolerance for geometries that need it. | |
| EGS_Float | halfBoundaryTolerance |
| vector< label > | labels |
| Labels. More... | |
| EGS_Application * | app |
| The application this object belongs to. | |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static string | type = "EGS_NDGeometry" |
| The geometry type. | |
 Static Protected Attributes inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry Static Protected Attributes inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry | |
| static int | error_flag = 0 |
| Set to non-zero status if a geometry problem is encountered. | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry Static Public Member Functions inherited from EGS_BaseGeometry | |
| static int | findRegion (EGS_Float xp, int np, const EGS_Float *p) |
| Find the bin to which xp belongs, given np bin edges p. More... | |
| static int | nMedia () |
| Get the number of media registered so far by all geometries. More... | |
| static const char * | getMediumName (int ind) |
| Get the name of medium with index ind. More... | |
| static int | addMedium (const string &medname) |
| Add a medium or get the index of an existing medium. More... | |
| static int | getMediumIndex (const string &medname) |
| Get the index of a medium named medname. More... | |
| static EGS_BaseGeometry * | createGeometry (EGS_Input *) |
| Create a geometry (or geometries) from a given input. More... | |
| static EGS_BaseGeometry * | createSingleGeometry (EGS_Input *inp) |
| Create a single geometry from the input inp. More... | |
| static void | clearGeometries () |
| Clears (deletes) all geometries in the currently active geometry list. More... | |
| static EGS_BaseGeometry * | getGeometry (const string &Name) |
| Get a pointer to the geometry named Name. More... | |
| static EGS_BaseGeometry ** | getGeometries () |
| static int | getNGeometries () |
| static string | getUniqueName () |
| Get a unique geometry name. More... | |
| static void | describeGeometries () |
| Describes all existing geometries. More... | |
| static void | setActiveGeometryList (int list) |
| Set the currently active geometry list. | |
| static int | getLastError () |
| static void | resetErrorFlag () |
Detailed Description
A class modeling a N-dimensional geometry.
To understand an N-dimensional geometry object, consider an XYZ-geometry made from sets of ![]() x-planes,
x-planes, ![]() y-planes and
y-planes and ![]() z-planes. This type of geometry is implemented in the DOSXYZnrc user code and is useful e.g. for the modeling of a computed tomography image of a patient undergoing radiotherapy. The sets of x-, y- and z-planes define
z-planes. This type of geometry is implemented in the DOSXYZnrc user code and is useful e.g. for the modeling of a computed tomography image of a patient undergoing radiotherapy. The sets of x-, y- and z-planes define ![]() parallelepiped regions (a.k.a. voxels) in space. The regions can be numbered in any way but it is customary to use the convention that when a position is in the
parallelepiped regions (a.k.a. voxels) in space. The regions can be numbered in any way but it is customary to use the convention that when a position is in the ![]() 'th x-planes region (i.e. between the
'th x-planes region (i.e. between the ![]() 'th and
'th and ![]() 'st x-plane), in the
'st x-plane), in the ![]() 'th y-planes region and in the
'th y-planes region and in the ![]() 'th z-planes region, it is in region
'th z-planes region, it is in region ![]() in the XYZ-geometry. A position is inside an XYZ-geometry if it is inside the x-planes (i.e. it is between the first and last x-plane), inside the y-planes and inside the z-planes. To calculate the distance to any boundary along a given direction (the howfar() method) for a position inside the XYZ-geometry, one calculates the distance
in the XYZ-geometry. A position is inside an XYZ-geometry if it is inside the x-planes (i.e. it is between the first and last x-plane), inside the y-planes and inside the z-planes. To calculate the distance to any boundary along a given direction (the howfar() method) for a position inside the XYZ-geometry, one calculates the distance ![]() to the x-planes, the distance
to the x-planes, the distance ![]() to the y-panes, the distance
to the y-panes, the distance ![]() to the z-planes and then takes the minimum of
to the z-planes and then takes the minimum of ![]() and
and ![]() . To calculate the minimum distance to a boundary in any direction (the hownear() method) for a position inside the XYZ-geometry, one calculates the minimum distances to a boundary in any direction to the x-planes, y-planes and z-planes and takes the minimum of the three distances. Consider now an RZ-geometry, i.e. a geometry made from
. To calculate the minimum distance to a boundary in any direction (the hownear() method) for a position inside the XYZ-geometry, one calculates the minimum distances to a boundary in any direction to the x-planes, y-planes and z-planes and takes the minimum of the three distances. Consider now an RZ-geometry, i.e. a geometry made from ![]() z-planes intersecting
z-planes intersecting ![]() concentric cylinders with their axis along the z-axis to form
concentric cylinders with their axis along the z-axis to form ![]() regions. As with the XYZ-geometry one can use the convention that when a position is inside the
regions. As with the XYZ-geometry one can use the convention that when a position is inside the ![]() 'th z-planes region and the
'th z-planes region and the ![]() 'th cylinder region, it is in the
'th cylinder region, it is in the ![]() 'th region of the RZ-geometry. To calculate the distance along a given direction to the RZ-geometry for an inside position, one calculates the distances
'th region of the RZ-geometry. To calculate the distance along a given direction to the RZ-geometry for an inside position, one calculates the distances ![]() to the planes and
to the planes and ![]() to the cylinders and takes the minimum of the two. The minimum distance to a boundary in any direction for an inside point is also calculated as the minimum of the corresponding distances to the planes and to the cylinders.
to the cylinders and takes the minimum of the two. The minimum distance to a boundary in any direction for an inside point is also calculated as the minimum of the corresponding distances to the planes and to the cylinders.
The above discussion should make it clear that, once the howfar(), hownear(), isInside(), etc., methods are available for planes and cylinders, the algorithms for calculating howfar(), hownear()}, isInside(), etc., is essentially the same for XYZ- and RZ-geometries, with the only difference that in the former case one uses 3 geometries to divide the space into regions (i.e one has a 3-dimensional geometry) and in the latter case only 2 geometries (i.e one has a 2-dimensional geometry).
An N-dimensional geometry is a generalization of this concept to an arbitrary number of geometries (dimensions) of arbitrary types (not just planes and/or cylinders): An N-dimensional geometry is a geometry type that is constructed from ![]() other geometries
other geometries ![]() defining
defining ![]() regions so that
regions so that
- The geometry consists of
 regions
regions - A point is inside the geometry if and only if it is inside all of the
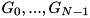 geometries.
geometries. - If a point is inside regions
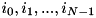 in
in 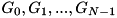 , it is inside the region
, it is inside the region 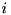 ,
,
in the N-dimensional geometry (as in the case of the XYZ and RZ examples above, this is just a convention that is convenient in practice).![\[ i = \sum_{j=0}^{N-1} i_j m_j~, \quad m_0 = 1~,~~~m_1 = n_0,~~~m_2 = n_0 n_1, ~~~ \cdots ~~~ m_i = m_{i-1} n_{i-1}~, \]](form_234.png)
- If the current position is in region
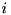 inside the N-dimension geometry, the distance
inside the N-dimension geometry, the distance 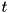 to a boundary in the N-dimension geometry along the direction of motion (needed by the howfar() method) is given by the minimum of the distances
to a boundary in the N-dimension geometry along the direction of motion (needed by the howfar() method) is given by the minimum of the distances 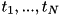 to a boundary in the geometries
to a boundary in the geometries 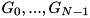 . If this minimum is given by the
. If this minimum is given by the 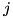 'th constituent geometry
'th constituent geometry 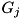 , the new region will be
, the new region will be 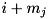 , unless the particle would exit
, unless the particle would exit 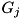 , in which case the new region is -1. (this is a direct consequence of the region numbering convention specified in the above equation).
, in which case the new region is -1. (this is a direct consequence of the region numbering convention specified in the above equation). - If the current position is outside of the N-dimensional geometry, the distances to the entry point is calculated as follows:
- If the position is outside of
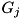 , calculate the distance
, calculate the distance 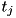 to the entry point of
to the entry point of 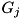
- If this distance exists (i.e. the trajectory intersects
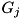 ), check if
), check if 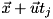 is inside all other geometries. If yes, exit the loop and return
is inside all other geometries. If yes, exit the loop and return 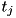
- Repeat a-b for all constituent geometries
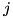 .
.
- If the position is outside of
This algorithm is also a generalization of the algorithms one uses to calculate distances to the boundary of XYZ-, RZ- and other 2 or 3 dimensional geometries.
- If the position is inside, the minimum perpendicular distance to a boundary
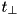 in the N-dimensional geometry in any direction (needed for the hownear() method) is given by the minimum of the perpendicular distances from all constituent geometries.
in the N-dimensional geometry in any direction (needed for the hownear() method) is given by the minimum of the perpendicular distances from all constituent geometries. - If the position is outside, the
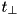 calculation is more complicated and depends upon the orthogonality of the constituent geometries. If the constituent geometries are considered to be orthogonal (more on this below),
calculation is more complicated and depends upon the orthogonality of the constituent geometries. If the constituent geometries are considered to be orthogonal (more on this below),
Here, the summation runs over all constituents
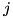 for which the position is outside. If the constituent geometries are not considered to be orthogonal, then
for which the position is outside. If the constituent geometries are not considered to be orthogonal, then 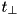 is the minimum of all perpendicular distances just as in the inside case. To understand this algorithm, consider a XYZ-geometry (which is an orthogonal geometry). If a position is e.g. inside the x- and y-planes but outside the z-planes, the nearest distance to a boundary in any direction is the perpendicular distance to the first or last z-plane (depending on which side the position is). If the position is inside the x-planes but outside of the y-planes and the z-planes, the nearest distance to a boundary in any direction is the distance to one of the edges of the XYZ-geometry and is given by
is the minimum of all perpendicular distances just as in the inside case. To understand this algorithm, consider a XYZ-geometry (which is an orthogonal geometry). If a position is e.g. inside the x- and y-planes but outside the z-planes, the nearest distance to a boundary in any direction is the perpendicular distance to the first or last z-plane (depending on which side the position is). If the position is inside the x-planes but outside of the y-planes and the z-planes, the nearest distance to a boundary in any direction is the distance to one of the edges of the XYZ-geometry and is given by 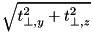 with
with 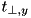 and
and 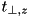 denoting the perpendicular distances to the y- and z-planes intersecting to form this edge. If the position is outside of all 3 plane sets, then the nearest distance to the XYZ-geometry is the distance to one of the corners, i.e.
denoting the perpendicular distances to the y- and z-planes intersecting to form this edge. If the position is outside of all 3 plane sets, then the nearest distance to the XYZ-geometry is the distance to one of the corners, i.e. 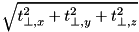 . Equation (1) is simply a generalization to
. Equation (1) is simply a generalization to 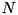 dimensions. Consider now a 2-dimensional geometry made from the intersection of cones with parallel planes. It is relatively easy to see that for the regions outside of the cones and the planes Eq. (1) overestimates the actual minimum distance in any direction (which is the distance to a point on the circle or ellipse formed by the intersection of the outer-most conical surface with the first or last plane). This geometry is therefore not considered to be orthogonal and one uses the minimum of the perpendicular distances to the planes and the cones.
dimensions. Consider now a 2-dimensional geometry made from the intersection of cones with parallel planes. It is relatively easy to see that for the regions outside of the cones and the planes Eq. (1) overestimates the actual minimum distance in any direction (which is the distance to a point on the circle or ellipse formed by the intersection of the outer-most conical surface with the first or last plane). This geometry is therefore not considered to be orthogonal and one uses the minimum of the perpendicular distances to the planes and the cones.
It should be clear from the above explanation of the implementation of the various geometry methods that an N-dimensional geometry can be constructed from any ![]() geometries provided that the underlying algorithms apply for the geometrical structure being modeled. An N-dimensional geometry is extremely useful and can be employed to model a wide range of geometries:
geometries provided that the underlying algorithms apply for the geometrical structure being modeled. An N-dimensional geometry is extremely useful and can be employed to model a wide range of geometries:
- An XYZ geometry where the three constituents are sets of x-, y- and z-planes.
- A RZ geometry where the two constituents are sets of z-cylinders and z-planes (it is of course possible to model a `‘RZ’' type geometry with an arbitrary orientation by using the any-axis and any-plane versions of the cylinder and plane sets)
- A polar coordinates geometry from sets of spheres and the EGS_ConeSet class with flag set to 2. This type of geometry is useful for instance in the calculation of point spread functions.
- One can construct hemi-spheres from a sphere and two planes, prisms with bases at any direction relative to the prism axis from the EGS_Prism class and one of the plane sets, cylinders with bases not perpendicular to the cylinder axis from a set of cylinders and one of the plane sets, cylinders divided into azimuthal segments from one of the cylinder classes and the EGS_IPlanes class, etc.
An N-dimensional geometry is defined using the following keys:
library = egs_ndgeometry dimensions = list of names of previously defined geometries hownear method = 0 or 1
All constituent geometries of the N-dimensional geometry must have been defined previously (i.e. their definition must appear before the definition of the N-dimensional geometry in the input file). The hownear() method input determines if the geometry constituents are considered to be orthogonal with 0 corresponding to orthogonal constituent geometries. It is very hard to automatically determine whether the constituents of an N-dimensional geometry are orthogonal and therefore it is the responsibility of the user to provide this input. Note, however, that the non-orthogonal hownear() version can always be used, it will just underestimate ![]() for orthogonal geometries and make the simulation run somewhat slower.
for orthogonal geometries and make the simulation run somewhat slower.
N-dimensional geometries are used in many of the example geometry files.
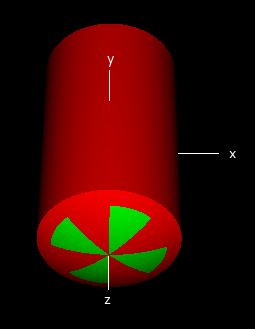
A simple example:
:start geometry definition:
# First dimension
:start geometry:
name = my_nd_iplanes
library = egs_iplanes
axis = 0 0 0 0 0 1
angles = 0 45 90 135
# No media required
:stop geometry:
# Second dimension
:start geometry:
name = my_nd_cylinders
library = egs_cylinders
type = EGS_ZCylinders
radii = 4 5
# No medium required
:stop geometry:
# Third dimension
:start geometry:
name = my_sphere
library = egs_spheres
midpoint = 0 0 0
radii = 10
:stop geometry:
# nd geometry
:start geometry:
name = my_nd
library = egs_ndgeometry
dimensions = my_nd_iplanes my_nd_cylinders my_sphere
hownear method = 1
:start media input:
media = water air water
set medium = 0 0
set medium = 1 1
set medium = 2 0
set medium = 3 1
set medium = 4 0
set medium = 5 1
set medium = 6 0
set medium = 7 1
:stop media input:
:stop geometry:
simulation geometry = my_nd
:stop geometry definition:
Optional Features
In order to use the gzip functionality you must have the egspp-geometry-lib-extras installed. Due to NRC licensing requirements this code is distributed separately and can be obtained from https://github.com/clrp-code/egspp-geometry-lib-extras/ .
Definition at line 315 of file egs_nd_geometry.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ EGS_NDGeometry() [1/2]
| EGS_NDGeometry::EGS_NDGeometry | ( | int | ng, |
| EGS_BaseGeometry ** | G, | ||
| const string & | Name = "", |
||
| bool | O = true |
||
| ) |
Construct a N-dimensional geometry from the ng dimensions G.
Definition at line 58 of file egs_nd_geometry.cpp.
References g, EGS_BaseGeometry::is_convex, EGS_BaseGeometry::isConvex(), N, n, EGS_BaseGeometry::nreg, and EGS_BaseGeometry::regions().
◆ EGS_NDGeometry() [2/2]
| EGS_NDGeometry::EGS_NDGeometry | ( | vector< EGS_BaseGeometry * > & | G, |
| const string & | Name = "", |
||
| bool | O = true |
||
| ) |
Construct a N-dimensional the array of dimensions G.
Definition at line 73 of file egs_nd_geometry.cpp.
References g, EGS_BaseGeometry::is_convex, EGS_BaseGeometry::isConvex(), N, n, EGS_BaseGeometry::nreg, and EGS_BaseGeometry::regions().
Member Function Documentation
◆ setMedia()
|
protectedvirtual |
Define media.
This function is re-implemented to permit easier media definition in a N-dimensional geometry.
Reimplemented from EGS_BaseGeometry.
Definition at line 114 of file egs_nd_geometry.cpp.
References egsWarning, EGS_Input::getInput(), EGS_BaseGeometry::med, N, EGS_BaseGeometry::setMedium(), and EGS_Input::takeInputItem().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- /home/rwtownson/EGSnrc/HEN_HOUSE/egs++/geometry/egs_nd_geometry/egs_nd_geometry.h
- /home/rwtownson/EGSnrc/HEN_HOUSE/egs++/geometry/egs_nd_geometry/egs_nd_geometry.cpp
 1.9.1
1.9.1